March 17, 2012
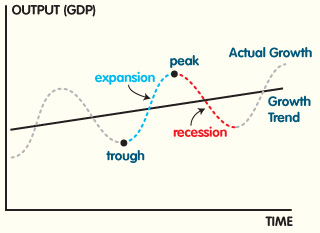
In the normal context of the business life cycle, a business, product, service or idea will progress through development, growth, peak and decline phases.
This cycle normally repeats over and over again as businesses usually adapt and change with the environment, close to the peak or into the decline phases. The resulting graph of a fairly healthy, adjusted business looks like waves increasing in height from left to right on the graph.
Current Business & Economic Climate
In addition to the phases of the normal business life cycle, other factors such as economic or global issues can alter the business life cycle. In the current economic climate over the past couple of years, those business cycles have either peaked or declined earlier than projected. In a recessionary period, many business cycles may be on the declining side, but as economies pull out a recession, cycles hit a low stabilization period and another growth period begins. Many businesses in 2012 are coming off the declining phase, reaching a low and are starting on the growth incline again. Some stock graphs sometimes mimic the business cycles of many corporations.
Business Cycle – Development Phase
This phase is the stomping ground for new product and business development. It is the research and development phase behind ventures, with heavy emphasis on planning, testing and piloting projects. In a repeating cycle this is a period of stabilization (as indicated by the trough on the graph), as companies have adjusted from declining phases and have stabilized operations and finances from a potential loss period.
Business Cycle – Growth Phase
 Following the development or stabilization period, companies and businesses enter a growth period, where new revenues grow from new products & services, or improvements made in operations. The growth, inclined phase indicated on the graph could be a result of efficiencies made in operations, to make businesses more competitive.
Following the development or stabilization period, companies and businesses enter a growth period, where new revenues grow from new products & services, or improvements made in operations. The growth, inclined phase indicated on the graph could be a result of efficiencies made in operations, to make businesses more competitive.
Business Cycle – Peak Phase
As products, services, ideas, and business reach maturity, they hit a peak phase where no further growth occurs. Peak phase may indicate no further revenue can be generated from products, or that the business has reached its maximum market penetration, or that the business may have reached maximum consumer interest. If you are keeping accurate, timely track of your finances and analyzing your trends, this would indicate that you may have to start making adjustments in business.
Business Cycle – Decline Phase
Many economists and business professionals have stated that the current global economic circumstances may have caused companies to enter the decline phase faster than projected. In the normal business cycle, if adjustments to business are not made, companies, products and ideas usually enter a deep decline period. The current economic climate may have accelerated that, but many statistics are indicating that the economies are turning around.
Business Cycles Repeat and Return to the Positive
As noted in the cycle, declining phases cause reactionary measures to once again achieve a period of stability. Following stable periods comes growth phases and the business cycle repeats on and on.
Business Tips for the Business Cycle
- Be aware of where your company, product, service or idea is within the business life cycle
- Keep track of your finances and operations and watch for trends as these trends are your indicators.
- Be pro-active rather than reactive; being pro-active to trends may help you recover easier and faster from declining phases
- Be cognizant of the business and economic climates locally, nationally and on a global basis
Business information, resources and tips for the entrepreneur
© 2012 Strategy Plan One



 u buy a brand, loyal customer base, standardized practices and operating procedures
u buy a brand, loyal customer base, standardized practices and operating procedures